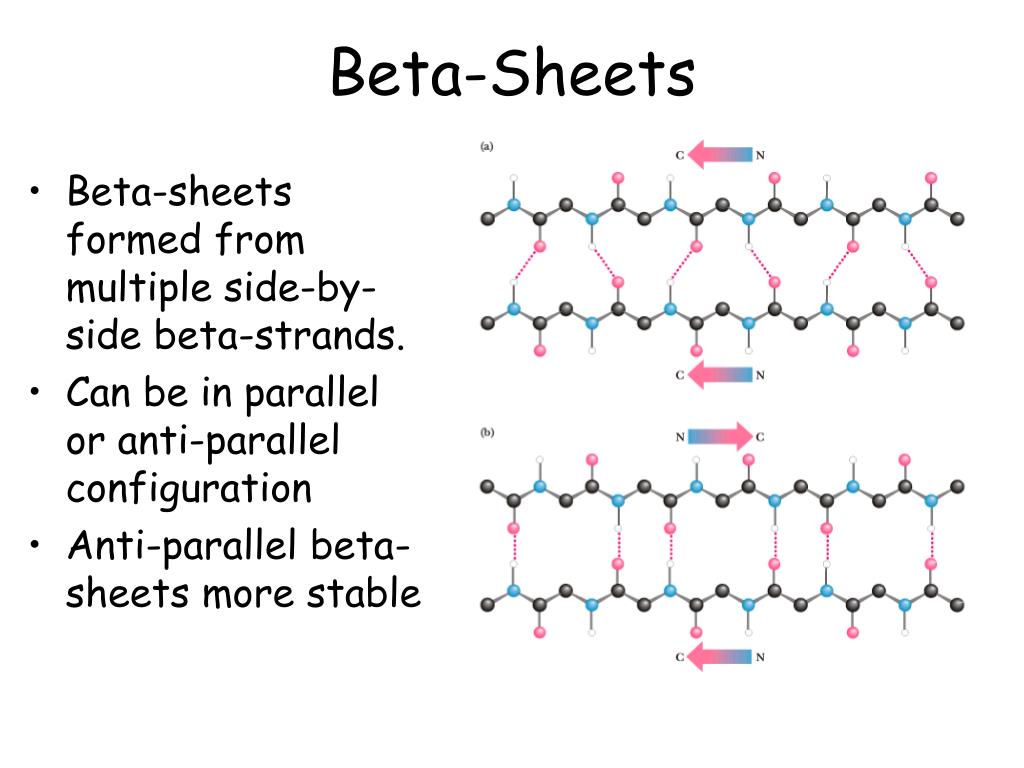
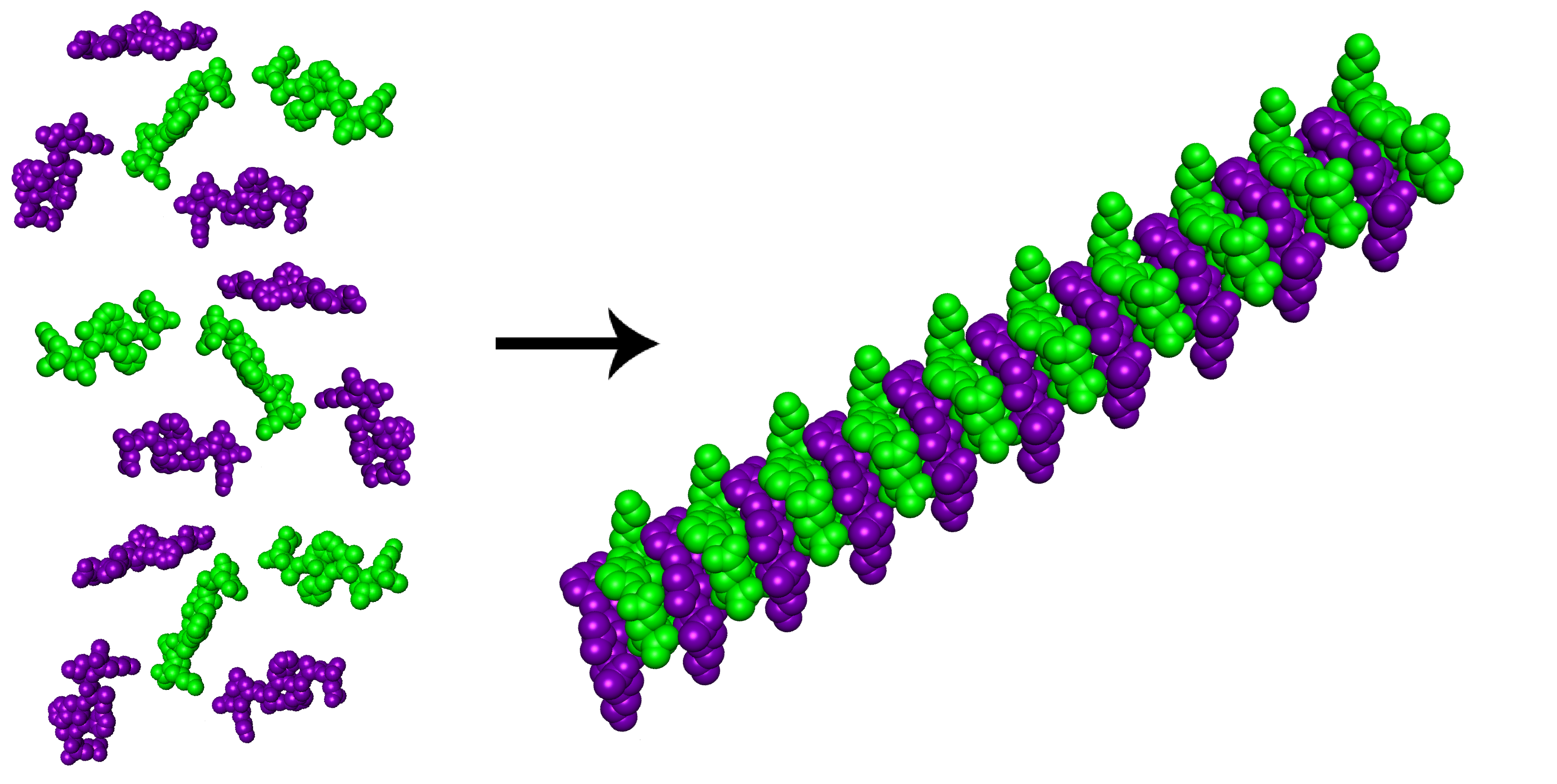
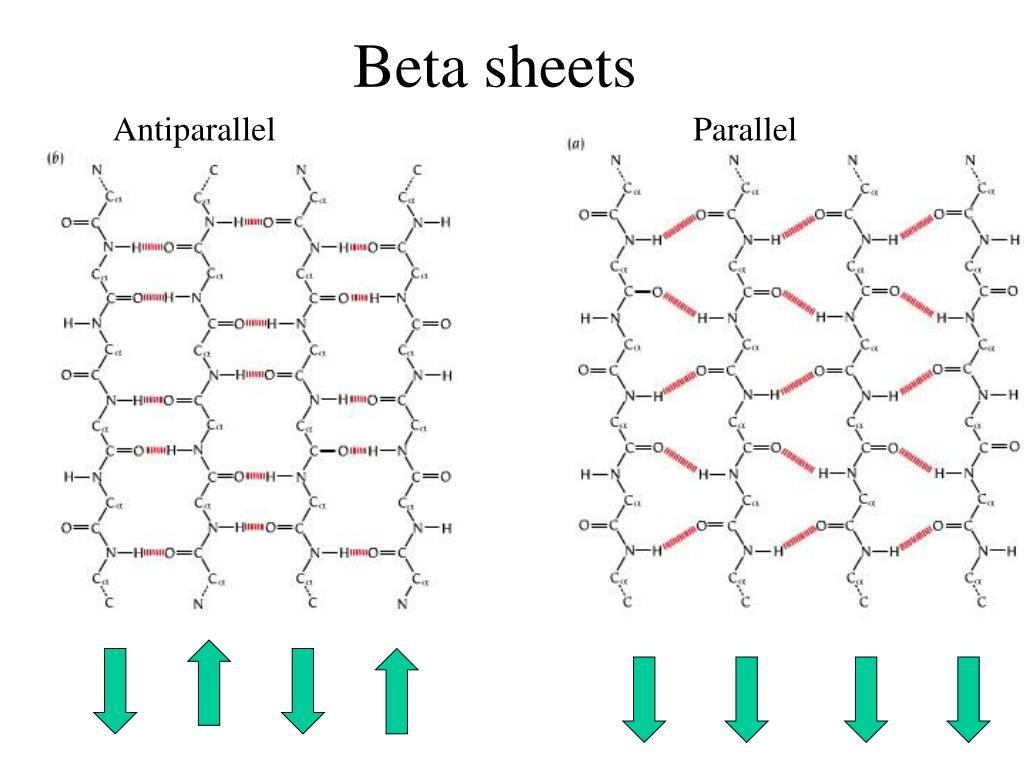
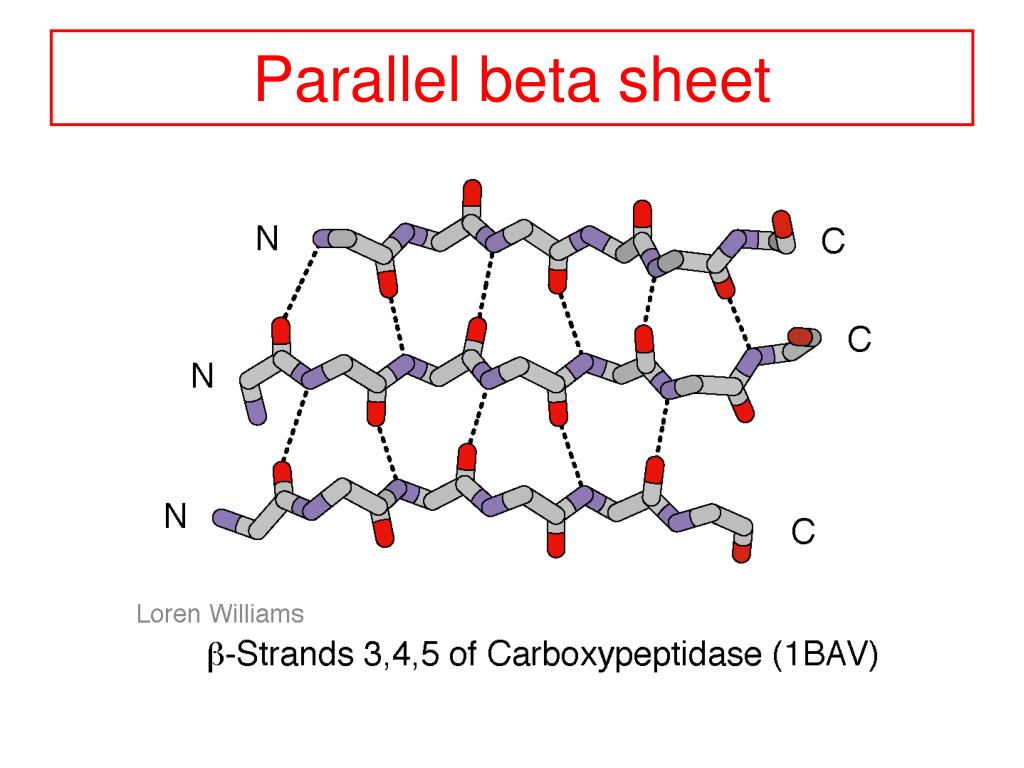
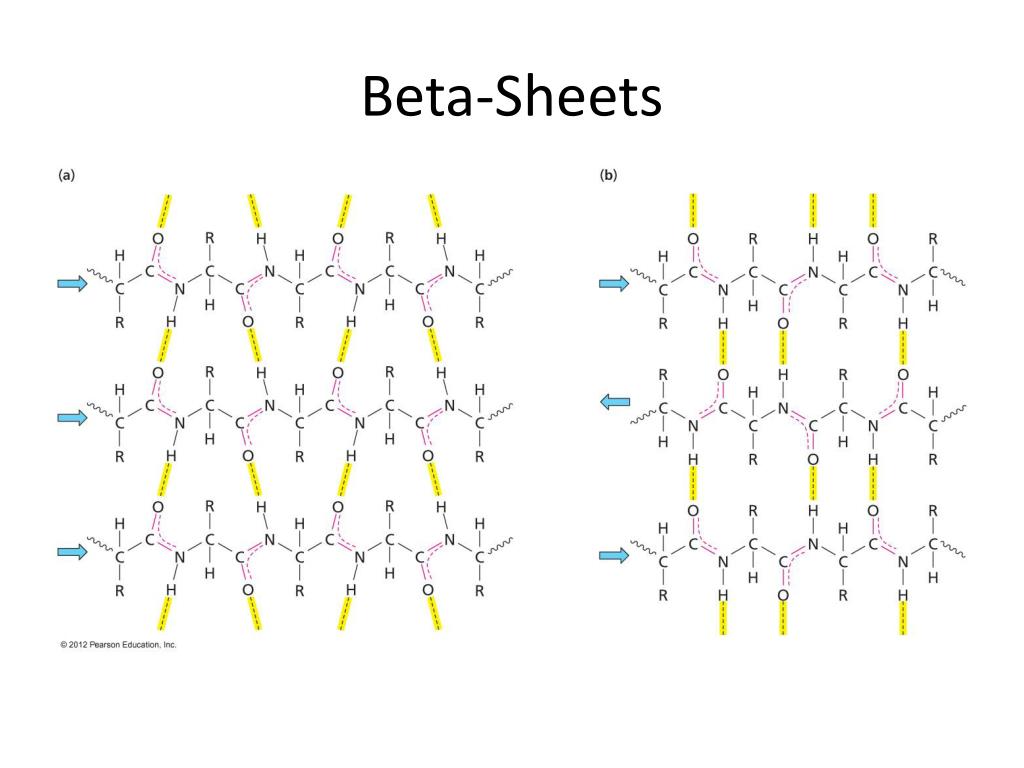
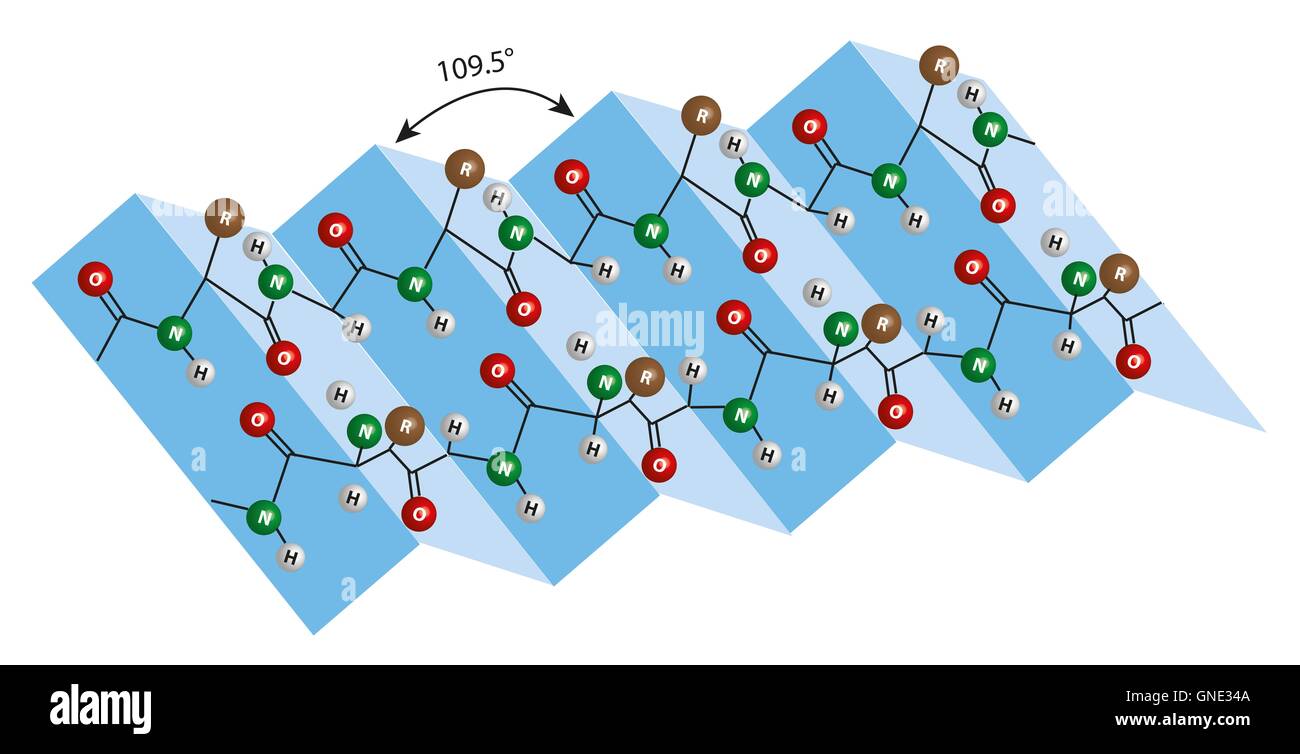
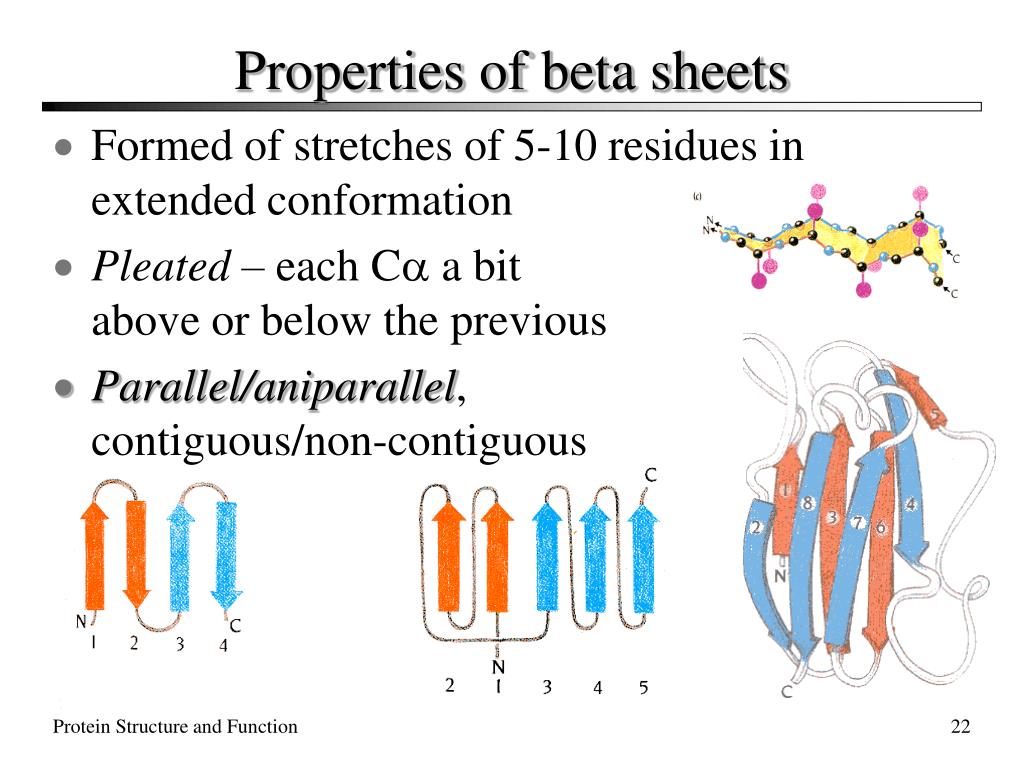
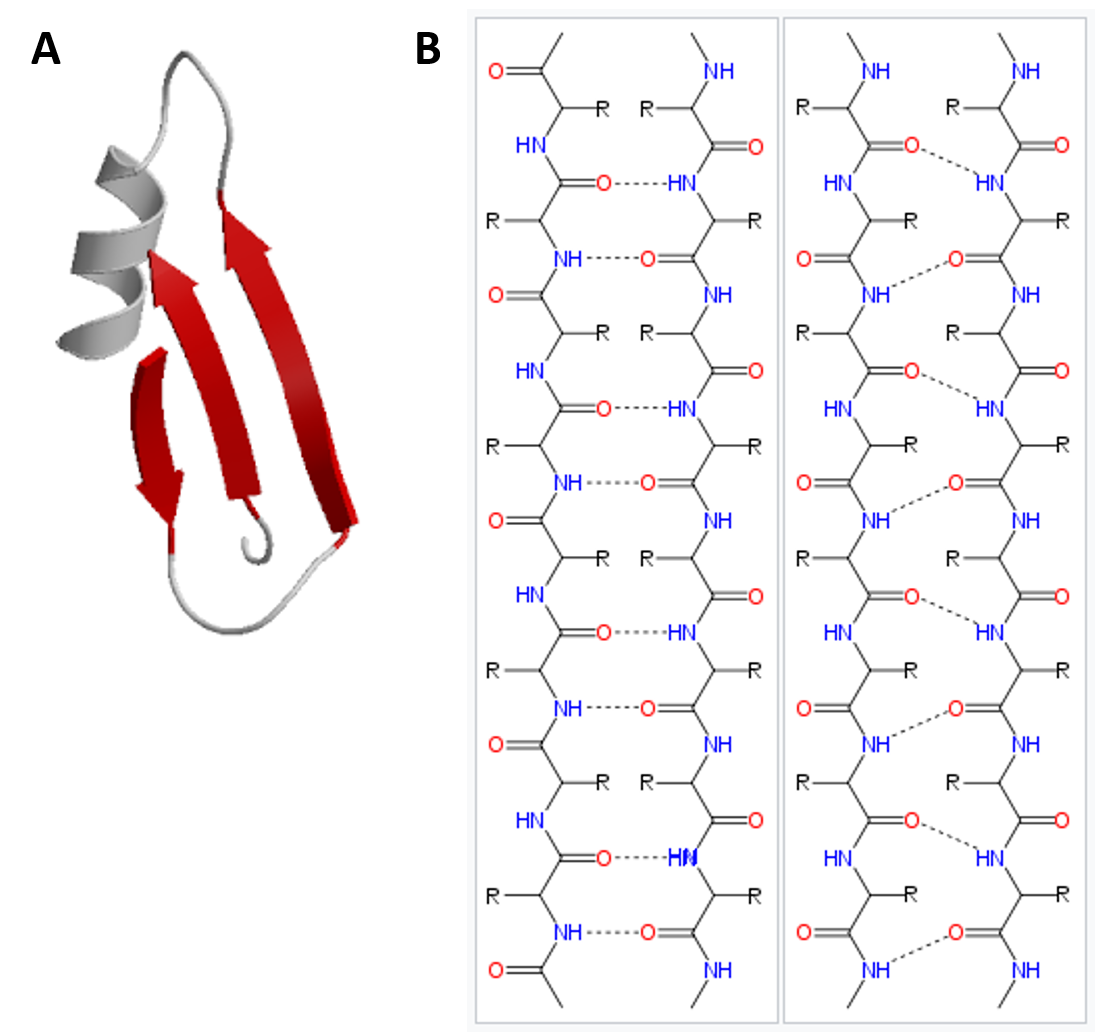
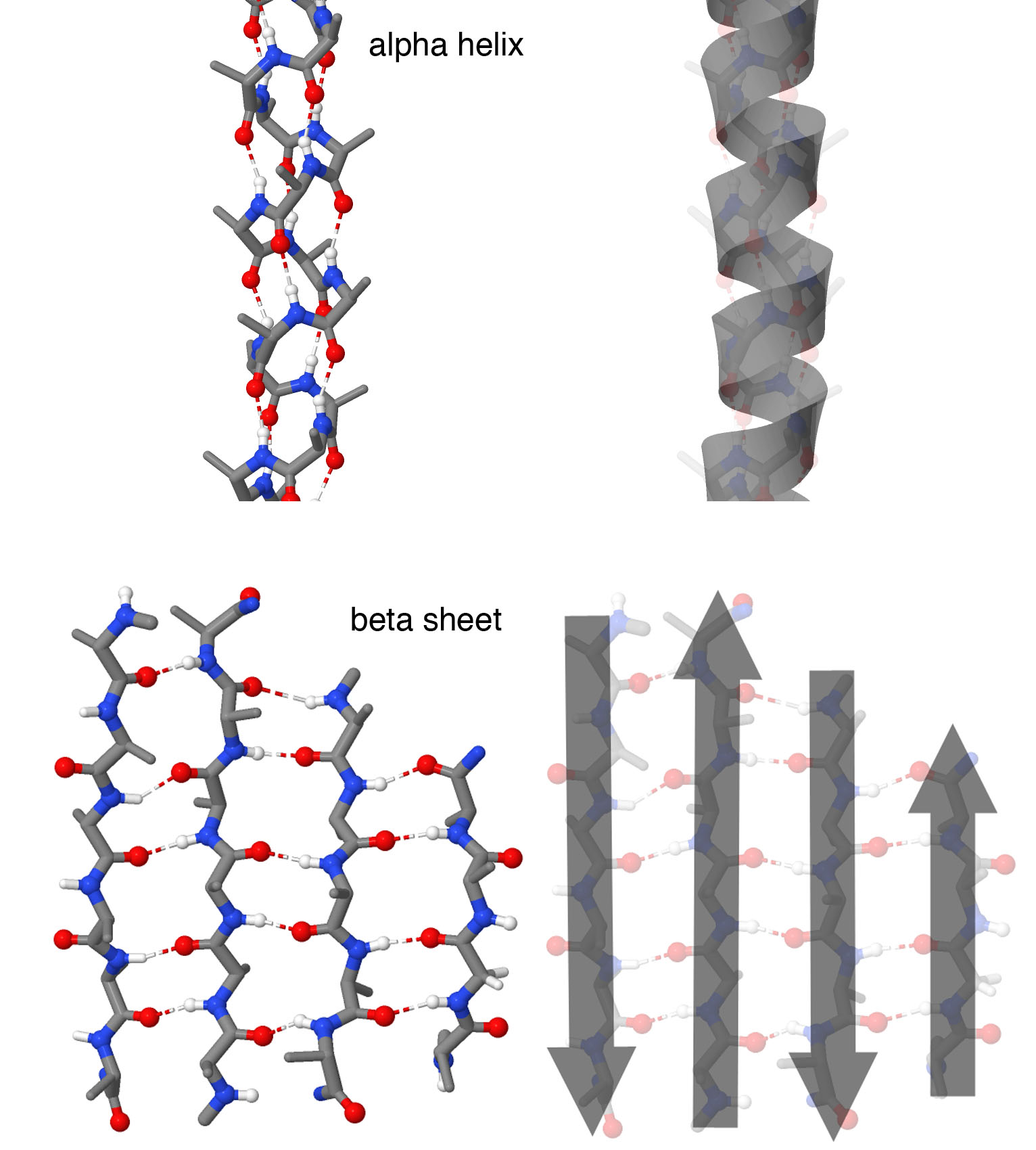
Beta Sheet - Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. This can occur in the presence of two consecutive proline residues, which create an. A beta strand is an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Adjacent beta strands can hydrogen bond to form a beta. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function.
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta strand is an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. This can occur in the presence of two consecutive proline residues, which create an. Adjacent beta strands can hydrogen bond to form a beta.
Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta strand is an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear. This can occur in the presence of two consecutive proline residues, which create an. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Adjacent beta strands can hydrogen bond to form a beta.
PPT Protein 3Dimensional Structure and Function PowerPoint
Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. This can occur.
What Are Beta Sheets Used For at Clifford Pannell blog
A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. Adjacent beta strands.
Beta Sheet Structure
A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. A beta strand is an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear. Adjacent beta strands can hydrogen.
PPT Introduction to Protein Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free
Adjacent beta strands can hydrogen bond to form a beta. Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes.
PPT Molecular Biophysics Lecture 2 Protein Structure II PowerPoint
Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta strand is an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear. Adjacent beta strands can hydrogen bond to form a beta. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of.
PPT Protein Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1462519
Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. This can occur.
Beta Sheet High Resolution Stock Photography and Images Alamy
Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. This can occur.
This can occur in the presence of two consecutive proline residues, which create an. Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Adjacent beta strands can hydrogen bond to form a beta. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. This can occur in the presence of two consecutive proline residues, which.
What Is A Beta Sheet
Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. A beta sheet consists of two or more beta strands linked by hydrogen bonds. A beta strand is an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how.
Adjacent Beta Strands Can Hydrogen Bond To Form A Beta.
Adjacent strands that form the beta sheet can either run in opposite directions (antiparallel beta sheet) or in the. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and overall protein function. This can occur in the presence of two consecutive proline residues, which create an. A beta strand is an element of secondary structure in which the protein chain is nearly linear.