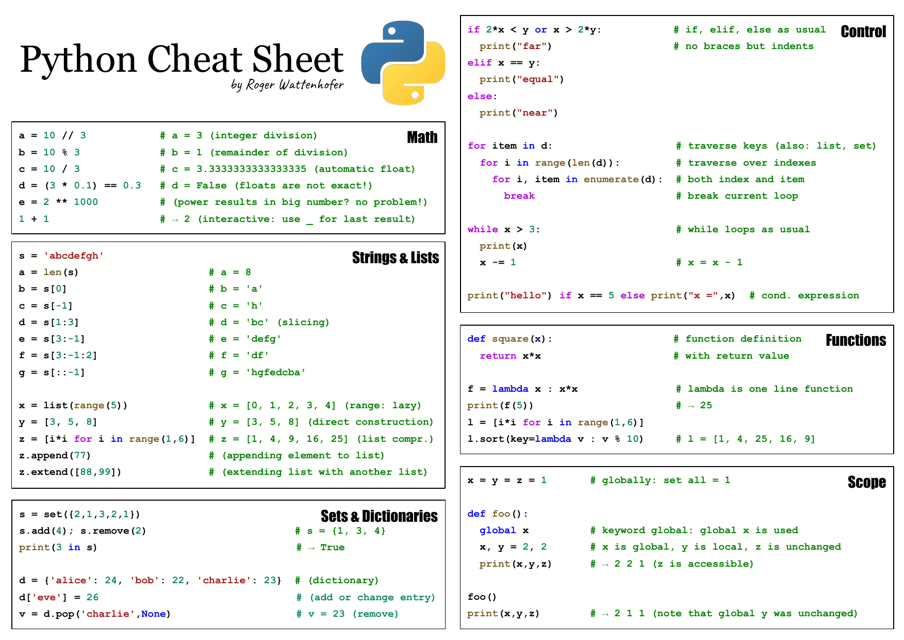
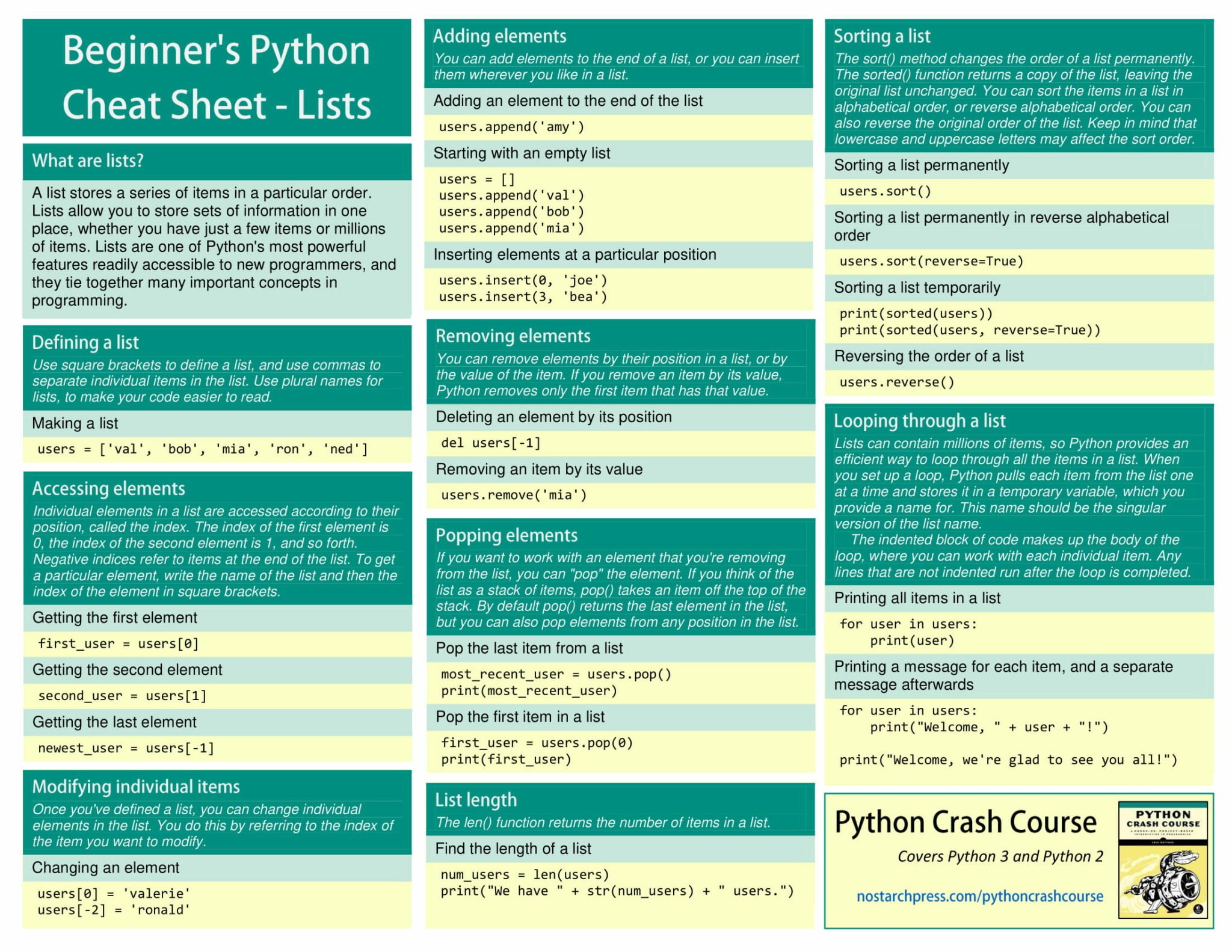
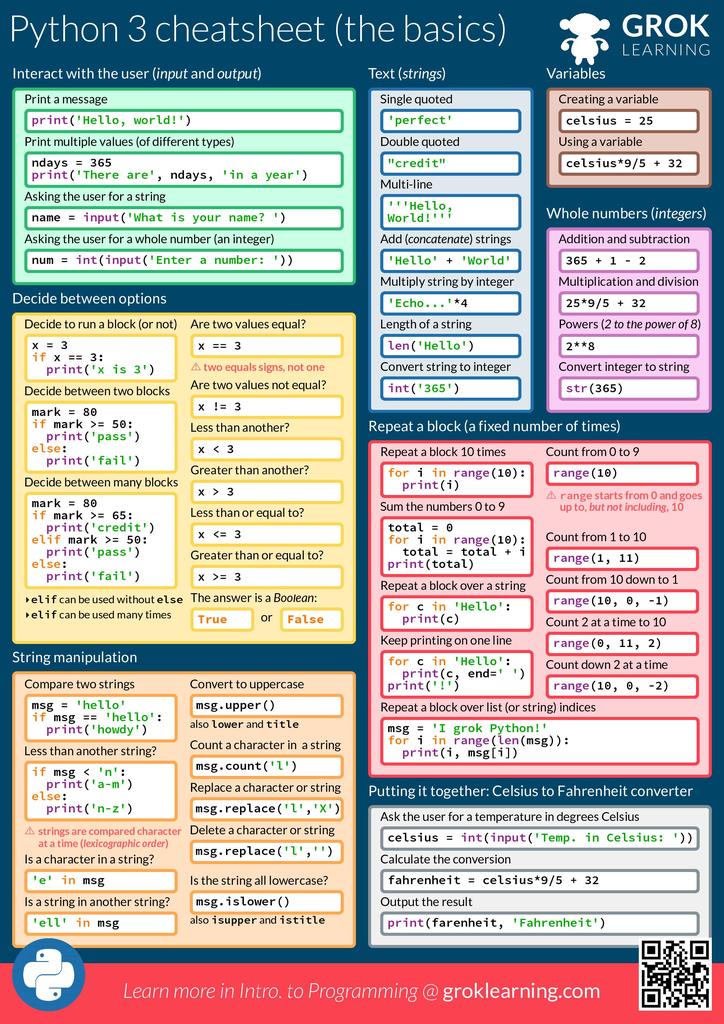
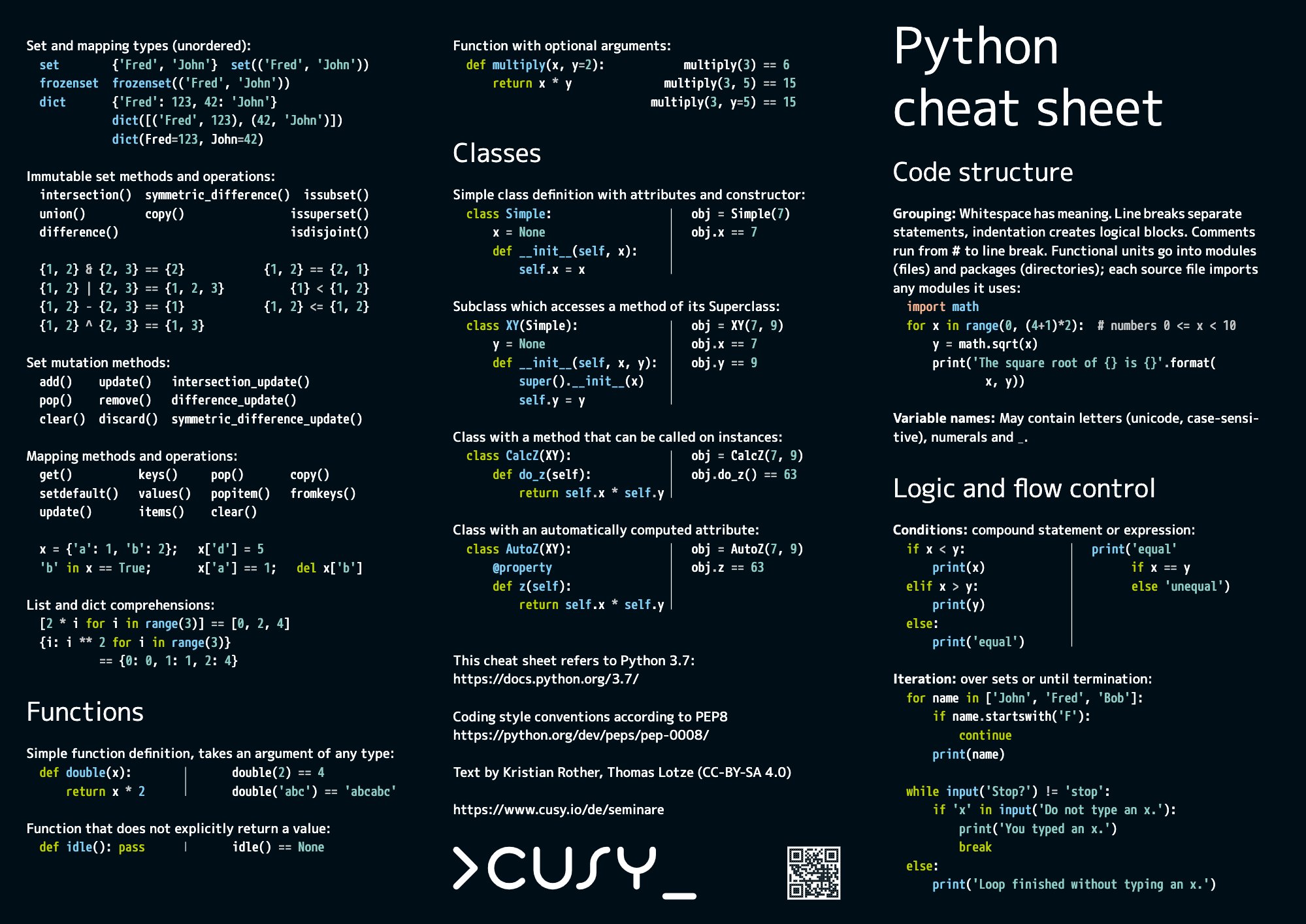
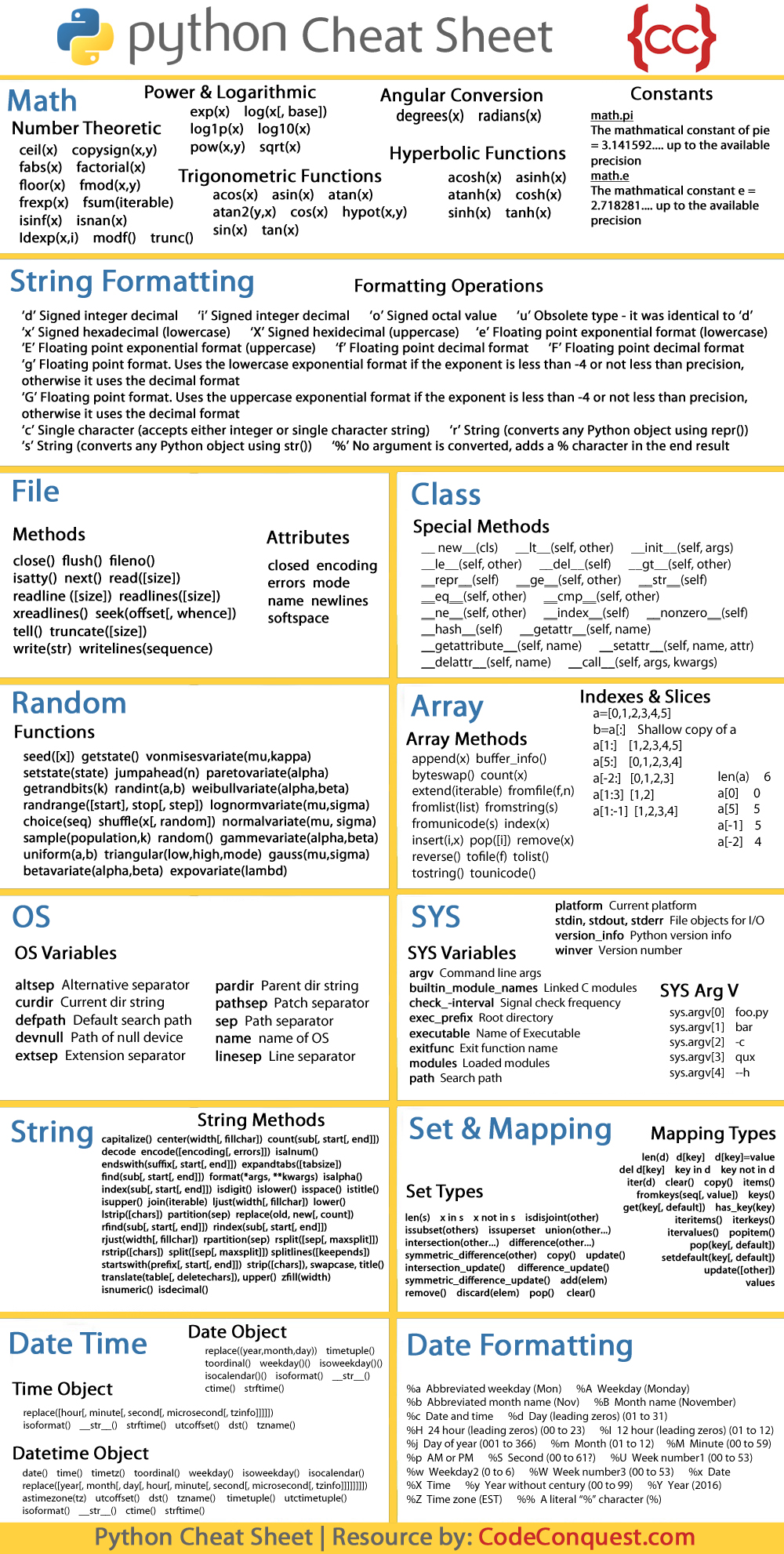
Cheat Sheet For Python - Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string.
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string.
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
BeginnersPythonCheatSheet8 (1) GlobalSQA
Representation string of x for display (cf. The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function.
Getting Started With Python Cheat Sheet Datacamp Bilarasa
The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Python Cheat Sheet Roger Wattenhofer Download Printable PDF
Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Python Leetcode Cheat Sheet sheet
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Basic Python Programming Language Poster Cheat Sheet Teaching Resource
The input() function always returns data as a string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
pythoncheatsheet.jpg
Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string.
a poster with some type of text and numbers on the back ground
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Printable Python Cheat Sheet
Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
Python Cheat Sheet for Beginners in 2024 Best Python Cheatsheet
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string. Representation string of x for display (cf.
NumPy Cheat Sheet Data Analysis In Python DataCamp, 47 OFF
We can receive input from the user by calling the input() function. The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string.
We Can Receive Input From The User By Calling The Input() Function.
The input() function always returns data as a string. Representation string of x for display (cf. Formatting on the back) = variables assignment char repr(x)→ . literal representation string.