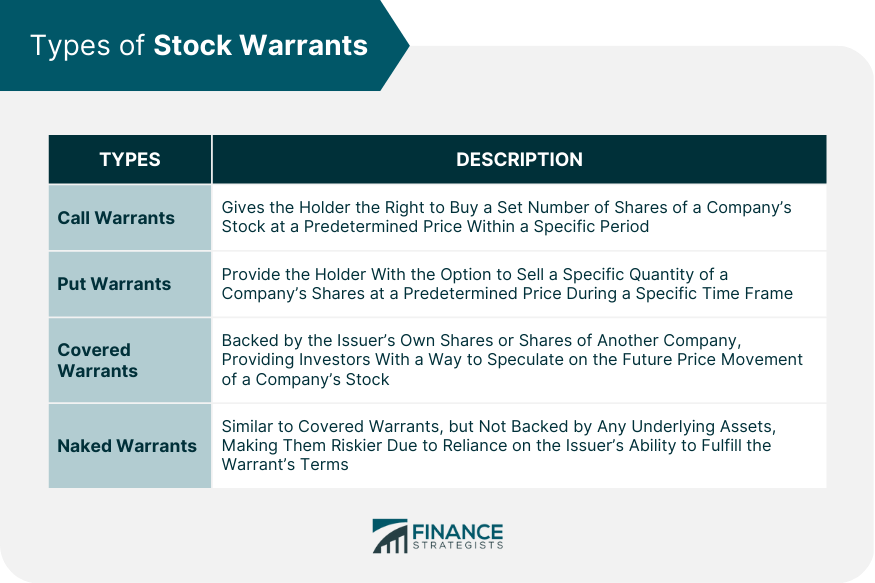
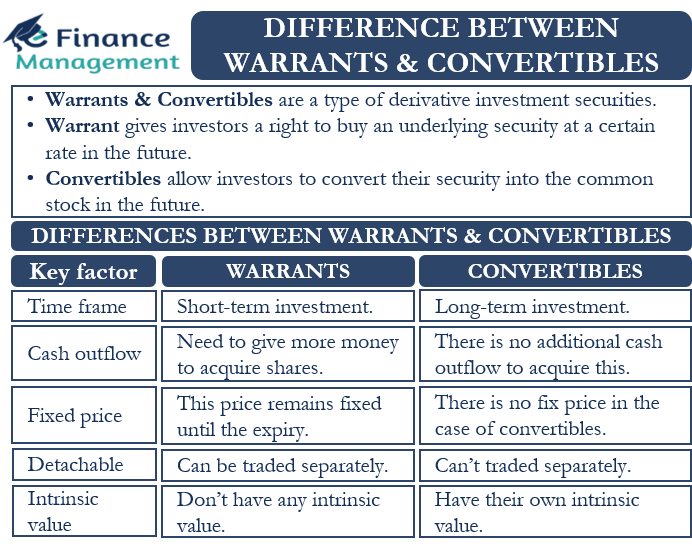
Financial Warrants Definition - Corporations often bundle warrants with another. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. What is a warrant in finance? A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the.
Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. What is a warrant in finance? Corporations often bundle warrants with another. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,.
A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. What is a warrant in finance? Corporations often bundle warrants with another. Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock.
PPT Warrants PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3518383
Corporations often bundle warrants with another. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. What is a warrant in finance? Warrants are traded as securities.
Derivative Warrants Explained Types and Example
What is a warrant in finance? Corporations often bundle warrants with another. Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to.
Warrants What are they and how do they work? Dandy Law
Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. What is a warrant in finance? A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed.
What Is a Stock Warrant? Definition, Types & Example TheStreet
What is a warrant in finance? A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset.
Stock Warrants Definition, How They Work, Types, Pros & Cons
Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. What is a warrant in finance? Corporations often bundle warrants with another. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing.
Warrants Illustration Explained Explanation View Financial Stock
Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. What is a.
What Is a Stock Warrant? Definition, Types, and How They Work • Match AH
A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. What is a warrant in finance? Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of.
Difference Between Warrants and Convertibles eFinanceManagement
Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. Corporations often bundle warrants with another. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of.
Warrants Free of Charge Creative Commons Financial 3 image
Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. What is a warrant in finance? Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed.
Warrant Define, Vs Options, Features Types eFinanceManagement
Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. Corporations often bundle warrants with another. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the. What is a warrant in finance? Warrants are traded as securities.
Corporations Often Bundle Warrants With Another.
Warrants are traded as securities whose price reflects the value of the underlying stock. What is a warrant in finance? Warrants are derivative financial instruments that offer investors the opportunity to buy or sell an underlying asset (such as shares,. A warrant is a financial security that permits the holder to purchase the issuing company’s underlying shares at a fixed price called the.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Warrant-00caae50e5e9440e96dbef0645750b1b.jpg)