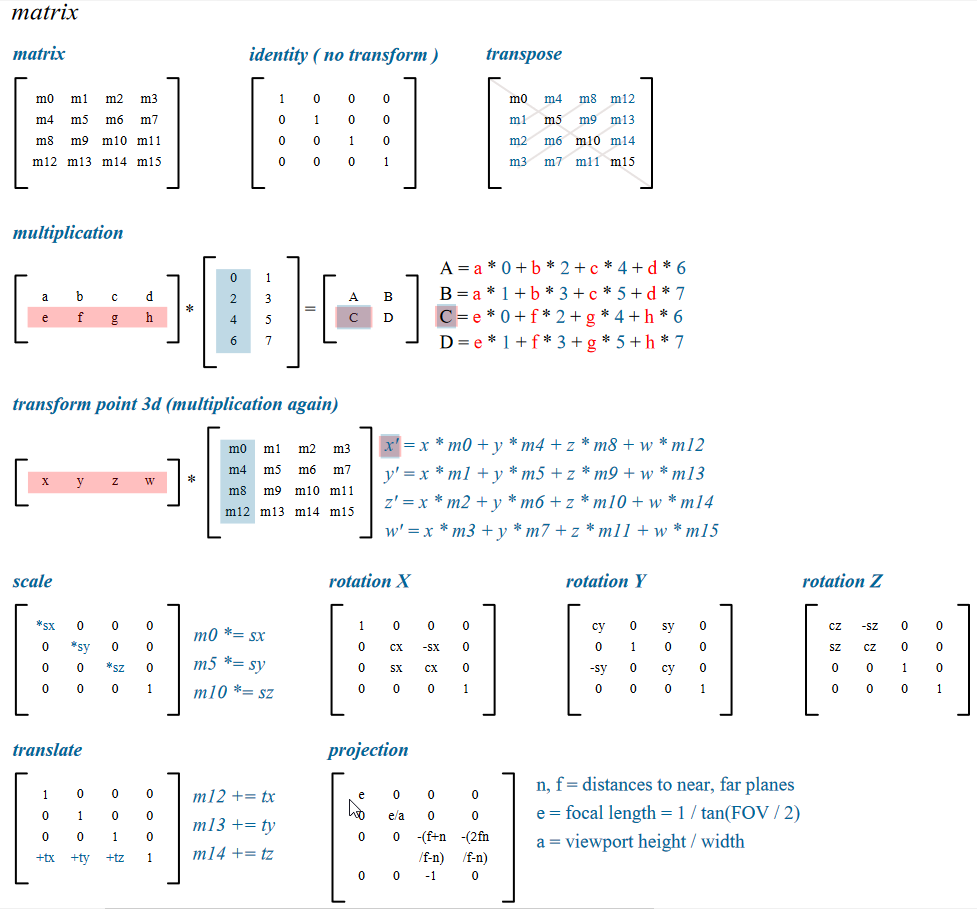
Matrix Cheat Sheet - If r = 0, then stop! Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual. In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x Arrange a and b so that a b. Key ingredients in our approach are polar duality in the sense of e ros and. We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory. For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5 8 + 1]︂ and √ 2 [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ = [︂. Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. That the elements of x are independent (e.g.
In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. That the elements of x are independent (e.g. Key ingredients in our approach are polar duality in the sense of e ros and. Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual. Note that it is always assumed that x has no special structure, i.e. The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory. Not symmetric, toeplitz, positive de nite). If r = 0, then stop! For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5 8 + 1]︂ and √ 2 [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ = [︂.
Arrange a and b so that a b. Not symmetric, toeplitz, positive de nite). If r = 0, then stop! That the elements of x are independent (e.g. Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory. Key ingredients in our approach are polar duality in the sense of e ros and. Note that it is always assumed that x has no special structure, i.e. Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual. We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b.
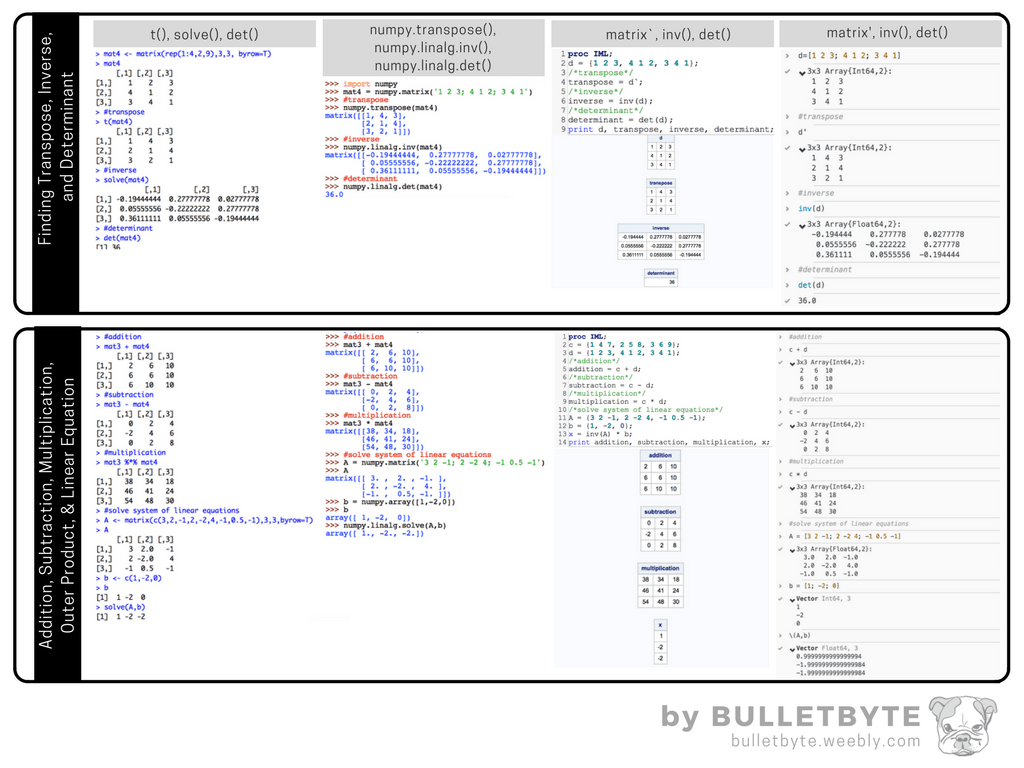
Cheat Sheet Matrix (Mathematics) Subroutine
We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. Note that it is always assumed that x has no special structure, i.e. Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual. The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps.
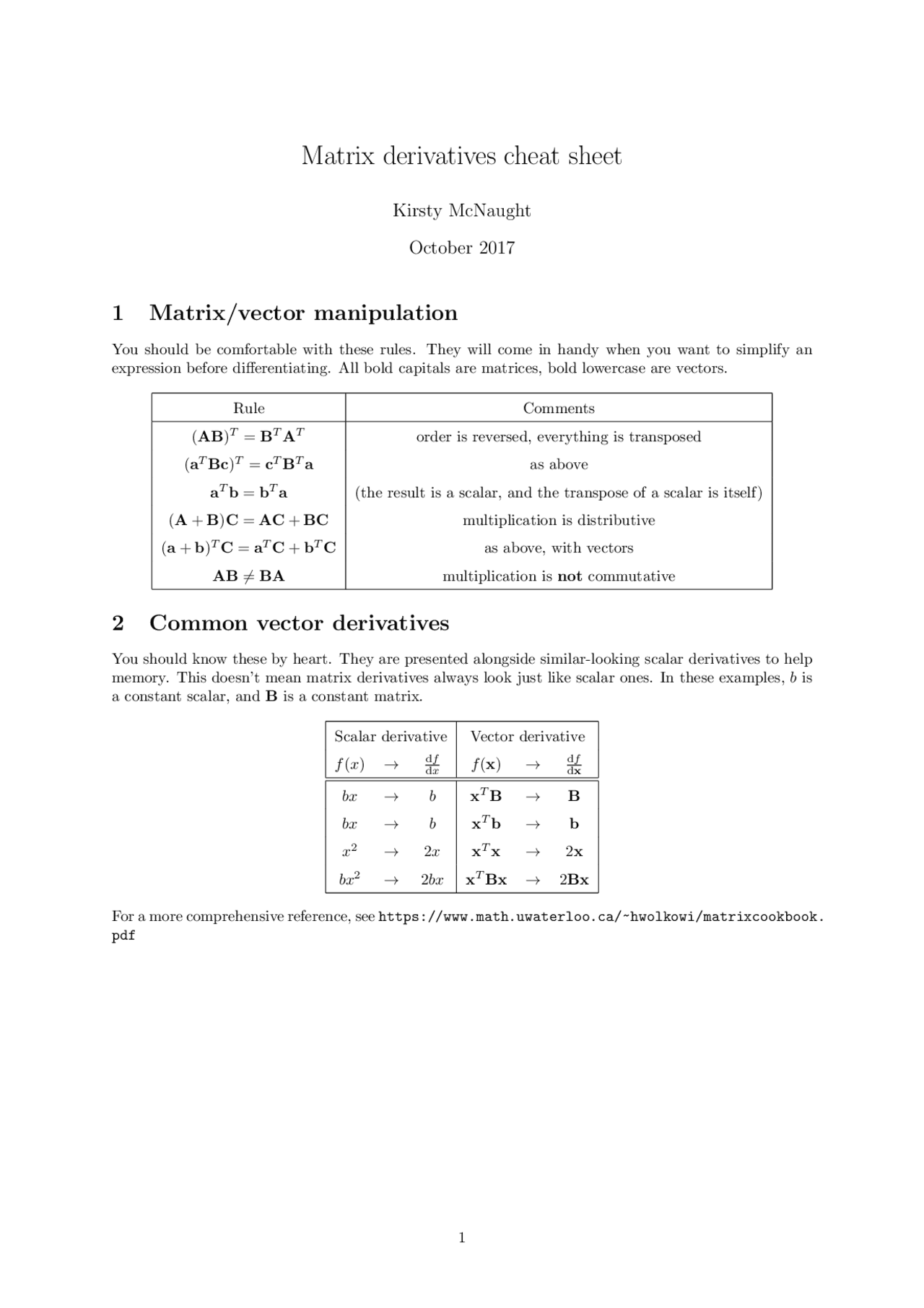
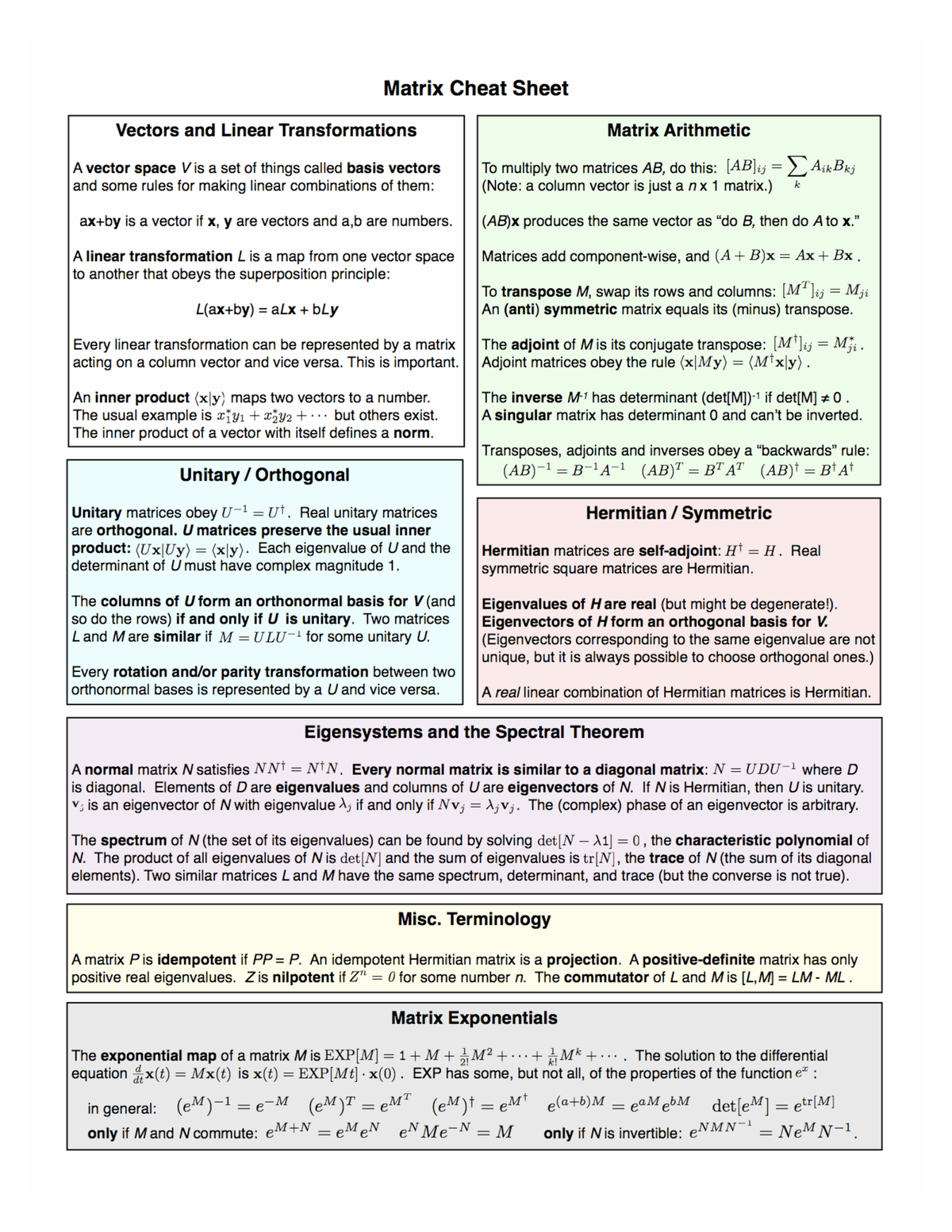
Matrix derivatives cheat sheet Docsity
Not symmetric, toeplitz, positive de nite). Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5.
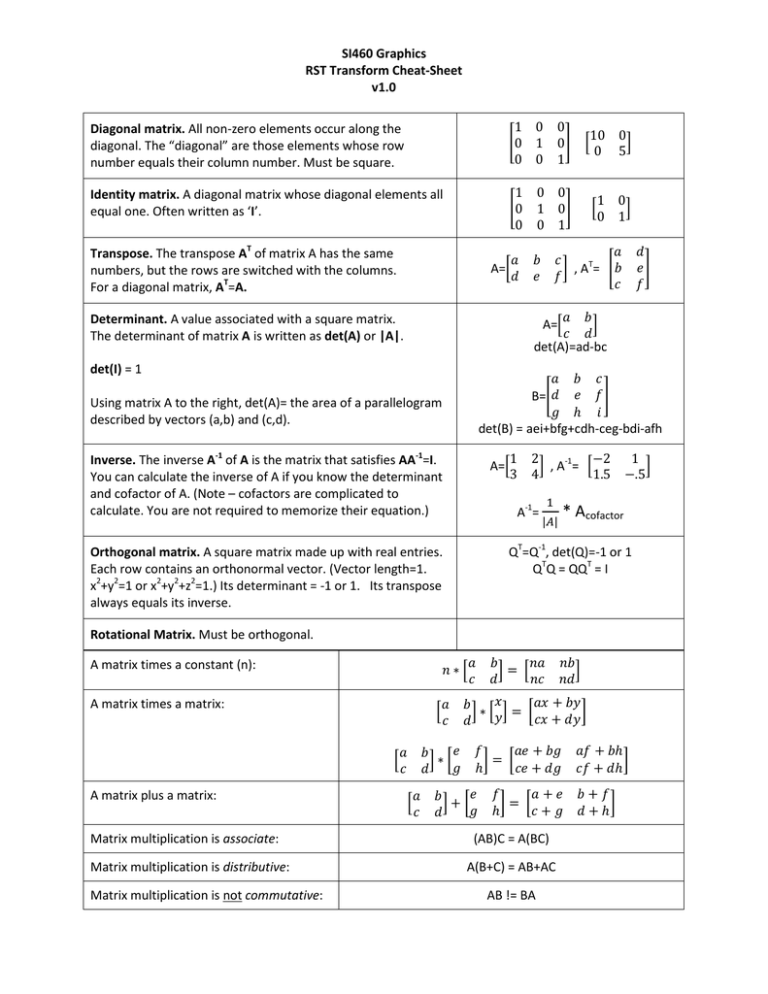
Matrix Cheat Sheet
Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. Not symmetric, toeplitz, positive de nite). In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5 8 + 1]︂ and √ 2 [︂.
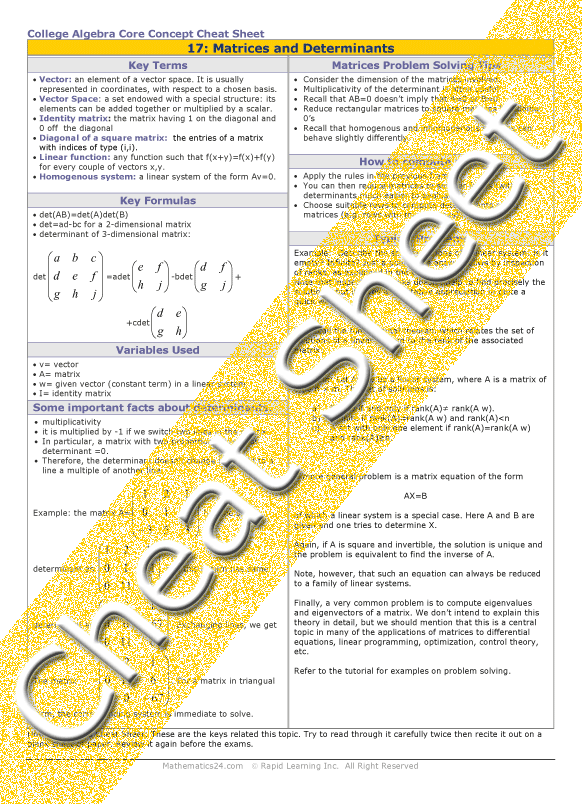
Matrices And Determinants Cheat Sheet
That the elements of x are independent (e.g. Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5 8 + 1]︂ and √.
Matrix Cheat Sheet
That the elements of x are independent (e.g. Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual. In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory. Arrange a and.
Matrix Cheat Sheet
That the elements of x are independent (e.g. For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5 8 + 1]︂ and √ 2 [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ = [︂. Note that it is always assumed that x has no special structure, i.e. In r 2 , the matrix for.
Matrix Cheat Sheet
We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory. Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition.
Matrix Cheat Sheet
Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual. Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory. For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ +.
Matrix Cheat Sheet Fundamentals of Mathematics Studocu
For instance, in 2×2(r), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5 8 + 1]︂ and √ 2 [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ = [︂. We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. Key ingredients in our approach are polar duality in the sense of e ros and. Not symmetric, toeplitz, positive de nite)..
Matrix Cheat Sheet
The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory. Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual. Arrange a and b so that a b. Not symmetric, toeplitz, positive de nite). Note that it is always assumed that x has no special structure, i.e.
Key Ingredients In Our Approach Are Polar Duality In The Sense Of E Ros And.
If r = 0, then stop! We get gcd(a;b) = gcd(b;0) = b. That the elements of x are independent (e.g. In r 2 , the matrix for a stretch by a factor of 2 in the x
Not Symmetric, Toeplitz, Positive De Nite).
Arrange a and b so that a b. Note that it is always assumed that x has no special structure, i.e. Write a = bq + r where 0 r < b. Addition and scalar multiplication are given by matrix addition and scalar multiplication of matrices as usual.
For Instance, In 2×2(R), [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ + [︂ 1 0 1 1]︂ = [︂ 3 5 8 + 1]︂ And √ 2 [︂ 2 5 7 ]︂ = [︂.
The geometry of matrix convex sets and their relationship to completely positive maps and dilation theory.