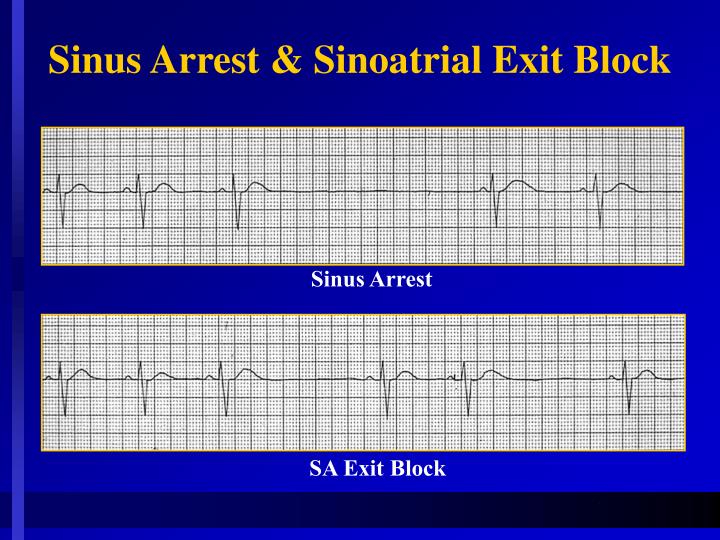
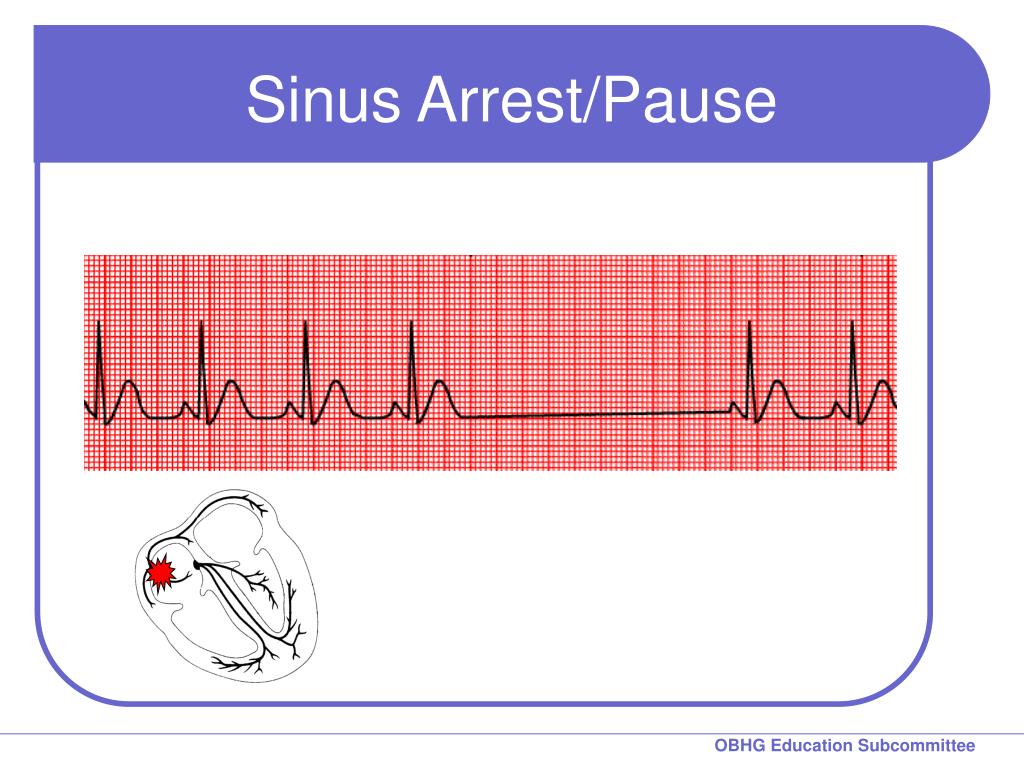
Sinus Pause Vs Sinus Arrest - This is often rescued by an escape. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium.
Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. This is often rescued by an escape. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse.
Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse. This is often rescued by an escape. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity.
ECG Educator Blog Sinus Arrest
Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse. This is often rescued by an escape. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or.
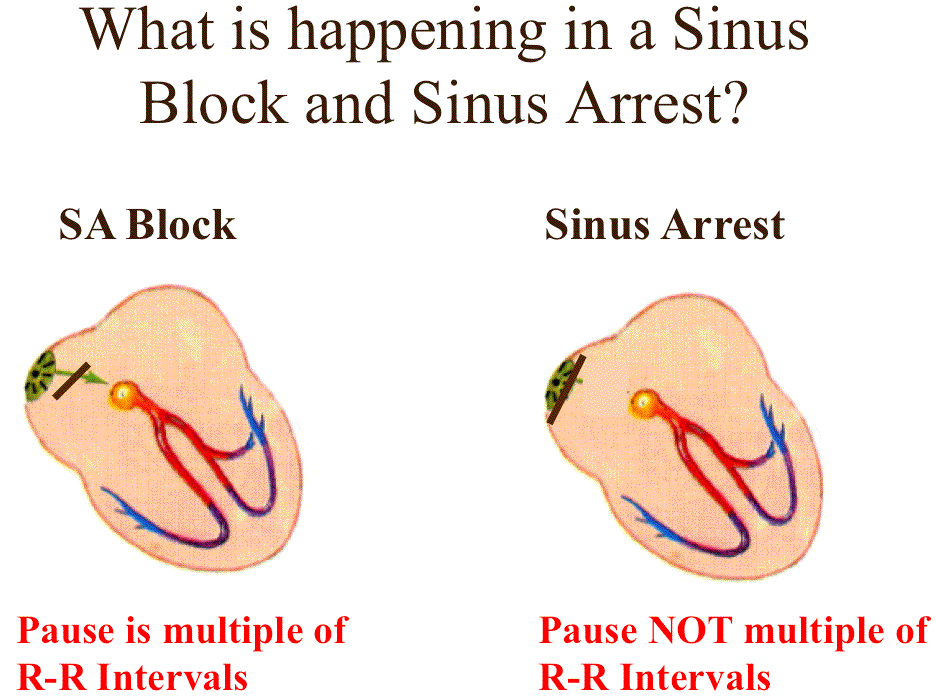
SA Block and Sinus Arrest
Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. This is often.
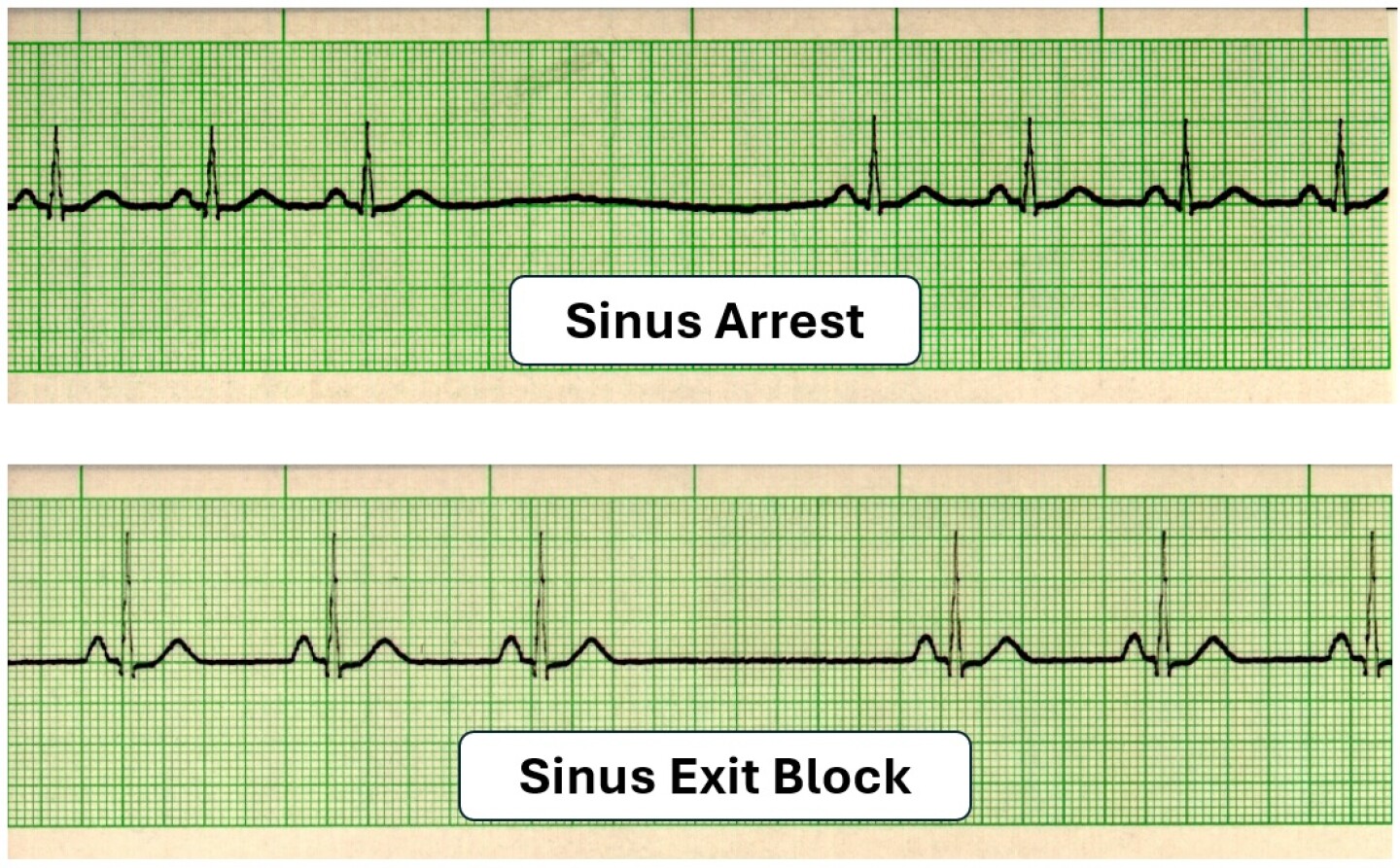
EKG Detective Sinus arrest vs. sinus exit block
Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn the difference between sinoatrial.
EKG Detective Sinus arrest vs. sinus exit block
Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse. This is often rescued by an escape. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the.
Sinus Rhythms BMH/Tele
Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. This is often.
PPT Brady Arrhythmia PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9503387
Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. This is often rescued by an escape. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without.
PPT Principles of Cardiac Pacing PowerPoint Presentation ID454515
This is often rescued by an escape. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without.
PPT Chapter 2 for 12 Lead Training RHYTHM PRACTICE PowerPoint
This is often rescued by an escape. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. Sinus pause or arrest where there are pauses of 3 seconds or more without atrial activity. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial.
Sinus Pause / Sinus Arrest YouTube
Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an.
Basic Ekg Reviewr2
Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an.
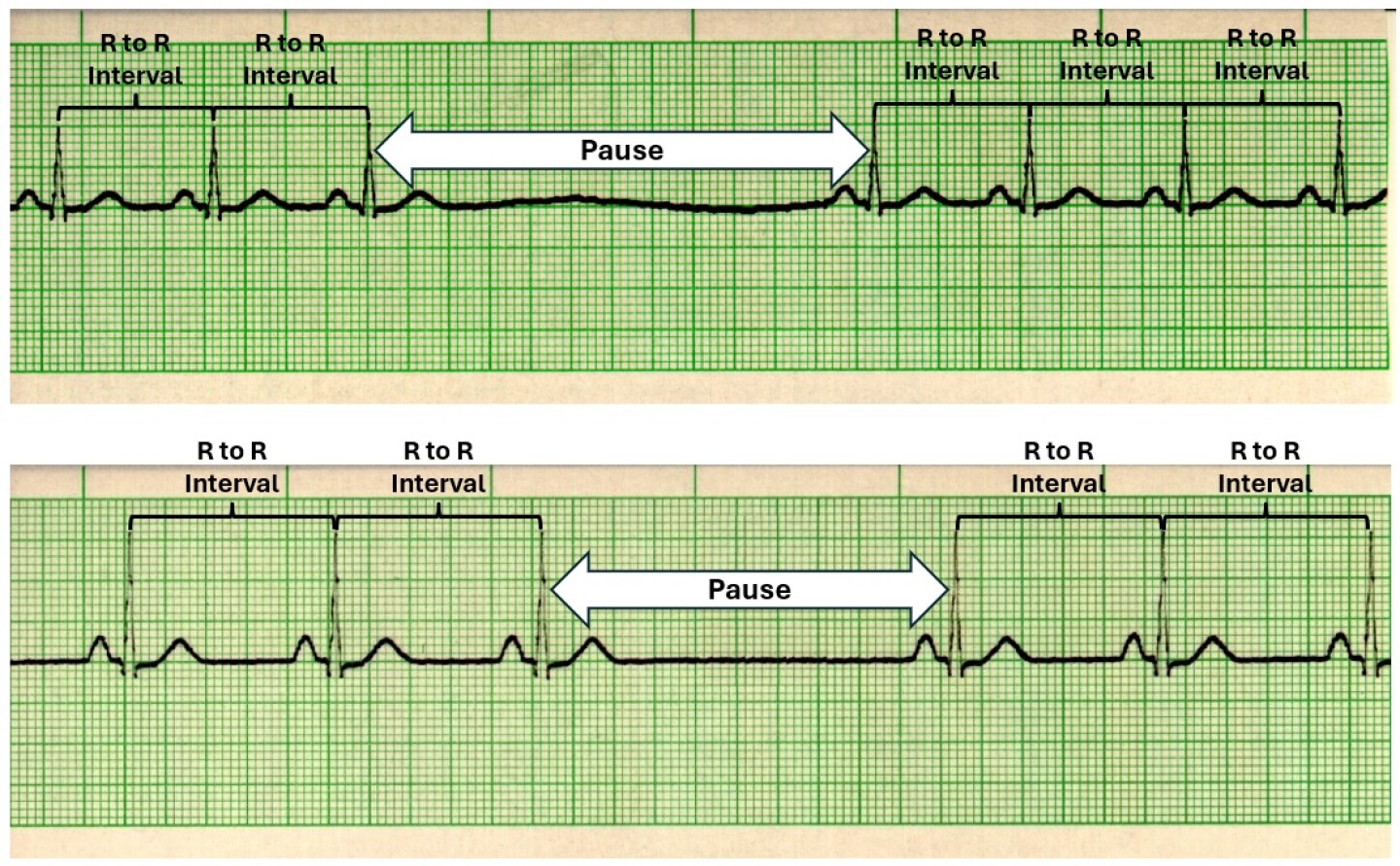
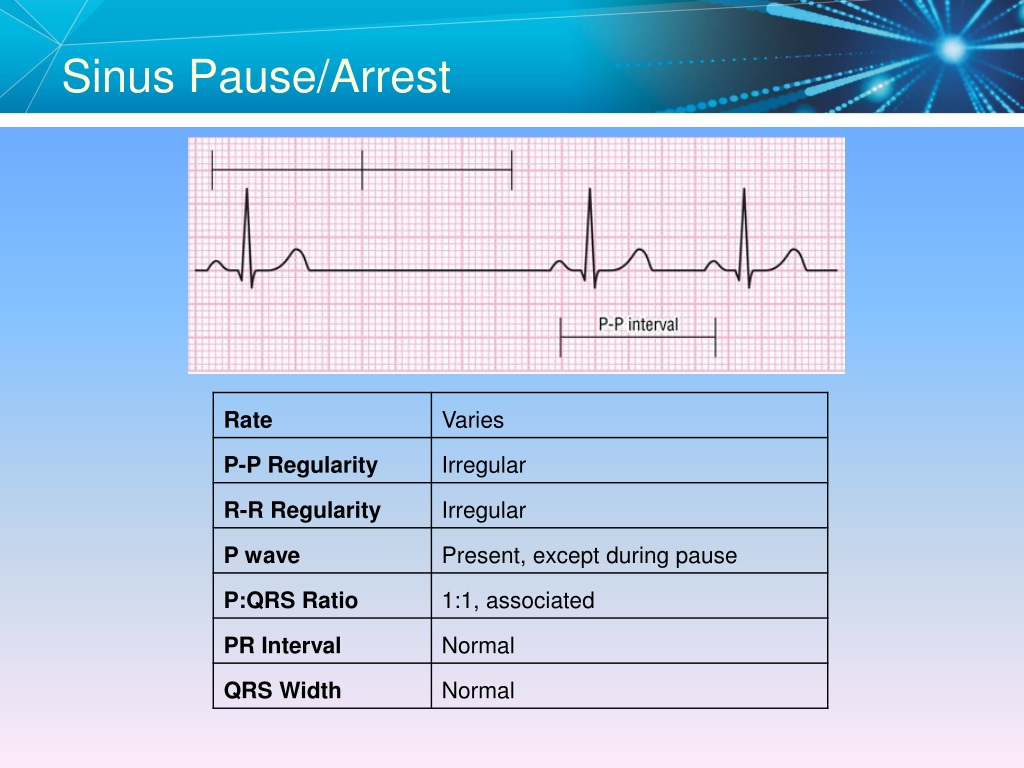
Sinus Pause Or Arrest Where There Are Pauses Of 3 Seconds Or More Without Atrial Activity.
Learn the difference between sinoatrial arrest and pause, which are arrhythmias caused by failure of the sinoatrial node to discharge an impulse. Patients with sa nodal dysfunction may be asymptomatic or highly symptomatic as in cases of sinus node dysfunction (snd;. Learn about pauses, a type of supraventricular arrhythmia caused by a conduction block in the sinus node or the atrium. This is often rescued by an escape.